Drug design, drug delivery and technologies, BioWorld Asia
Drug design, drug delivery & technologies
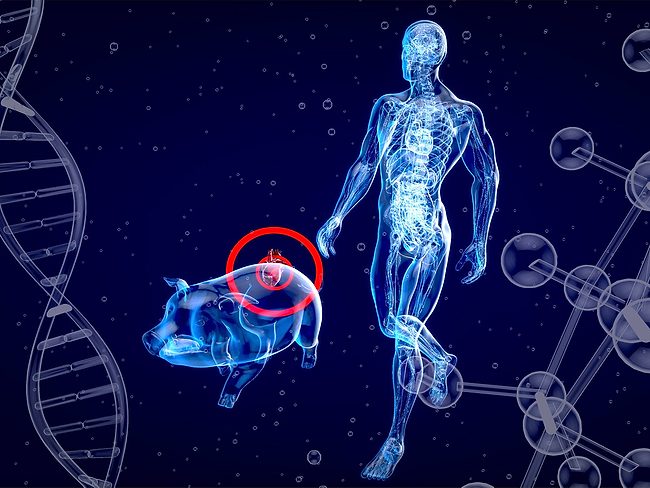
Ten days of normal survival of a pig liver in a human being
Read MoreDrug design, drug delivery & technologies
Intranasal bacterium for targeted brain delivery
Read MoreDrug design, drug delivery & technologies
More than 100M cells included in the human cell atlas
Read MoreDrug design, drug delivery & technologies
Chemistry Nobel awarded for 3D protein design, prediction work
Read MoreDrug design, drug delivery & technologies
Chemistry Nobel awarded for 3D protein design, prediction work
Read MoreDrug design, drug delivery & technologies