BioWorld - Thursday, December 25, 2025
ARTICLES
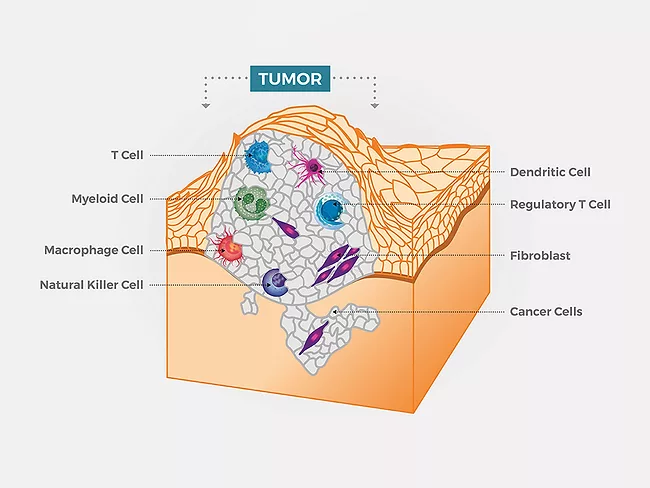
Immuno-oncology
Fragile X protein FMRP is major player in antitumor immunity
Nov. 22, 2022
Genetic/Congenital
In assessing shared genetic risk, love can look like pleiotropy
Nov. 18, 2022
Genetic/Congenital
Study hits shared risk between schizophrenia, bipolar disease on the nose
Nov. 15, 2022
SITC 2022
Business is shaky, but science is groundbreaking for engineered T-cell study
Nov. 11, 2022
Endocrine/Metabolic
AASLD 2022: Robust microbiome engineering enables mechanistic insights
Nov. 7, 2022