BioWorld - Tuesday, February 17, 2026
ARTICLES
‘22 in review
Progress in cancer, from brain metastases to cancer’s brain
Dec. 29, 2022
By Anette Breindl and Mar de Miguel
Cancer
‘22 in review: Progress in cancer, from brain metastases to cancer’s brain
Dec. 29, 2022
By Anette Breindl and Mar de Miguel
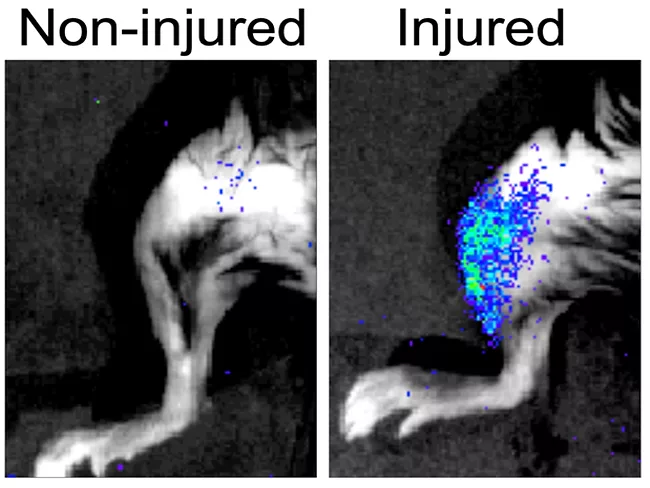
Musculoskeletal
Senescent cells are toxic to their neighbors, prevent muscle regeneration
Dec. 22, 2022
Neurology/Psychiatric
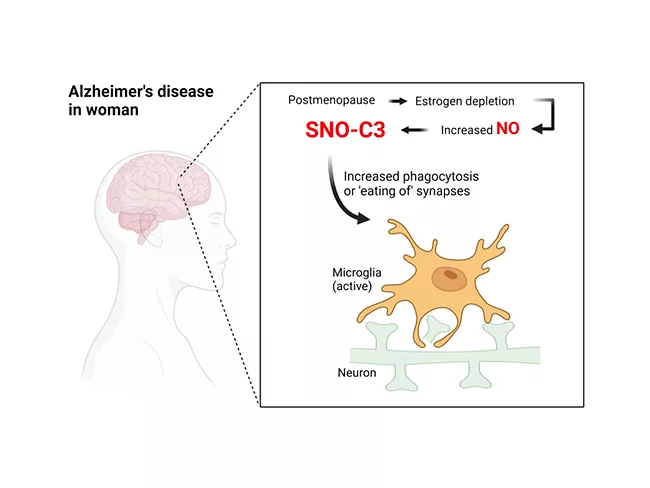
Nitric oxide-modified proteins reveal sex differences in Alzheimer’s
Dec. 19, 2022
Endocrine/Metabolic
Suppression of the somatotrophic axis controls liver damage but produces fibrosis
Dec. 14, 2022
Drug Design, Drug Delivery & Technologies
Synthetic cell junctions allow tissue reconstruction
Dec. 13, 2022