Science
Artificial intelligence
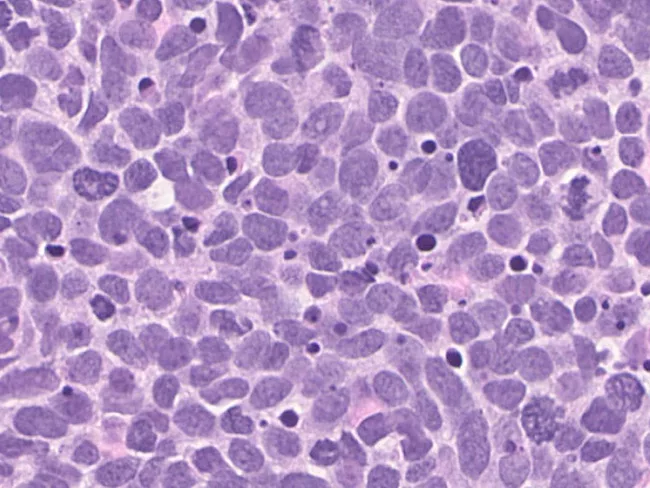
New AI model simultaneously predicts risk of getting 1,000 diseases
Read MoreDrug design, drug delivery & technologies
Cancer vaccines face collateral damage of mRNA funding cuts
Read MoreDrug design, drug delivery & technologies